若栈采用顺序存储方式,现有两栈共享空间V[1..n], top[i]代表i( i=1,2)个栈的栈顶(两个栈都空时top[1]= 1、top[2]= n),栈1的底在V[1],栈2的底在V[n],则栈满(即n个元素暂存在这两个栈)的条件是( )。
A. top[1]= top[2]
B. top[1]+ top[2]==1
C. top[1]+ top[2]==n
D. top[1]- top[2]== 1
Why is( )fun? What delights may its practitiopect as his reward? First is the sheer joy of making things. As the child delights in his mud pie, so the adult enjoys building things, especially things of his own design. Second is the pleasure of making things that are useful to other people. Third is the fascination of fashioning complex puzzle-like objects of interlocking moving parts and watching them work in subtle cycles, playing out the consequences of principles built in from the beginning. Fourth is the joy of always learning, which springs from the( )nature of the task. In one way or another the problem is ever new, and its solver learns something:sometimes( ), sometimes theoretical, and sometimes both. Finally, there is the delight of working in such a tractable medium. The( ), like the poet, works only slightly removed from pure thought-stuff. Few media of creation are so flexible, so easy to polish and rework, so readily capable of realizing grand conceptual structures.
Yet the program( ), unlike the poet’s words, is real in the sense that it moves and works, producing visible outputs separate from the construct itself. It prints results, draws pictures, produces sounds, moves arms.Programming then is fun because it gratifies creative longings built deep within us and delights sensibilities we have in common with all men.
第 1 问
A. programming
B. composing
C. working
D. writing
第 2 问
A. repeating
B. basic
C. non-repeating
D. advance
第 3 问
A. semantic
B. practical
C. lexical
D. syntactical
第 4 问
A. poet
B. architect
C. doctor
D. programmer
第 5 问
A. construct
B. code
C. size
D. scale
下图是HTML文件test.html在IE中的显示效果,实现图中①处效果的HTML语句是( ),实现图中②处效果的HTML语句是( ),实现图中③处效果的HTML语句是( )。
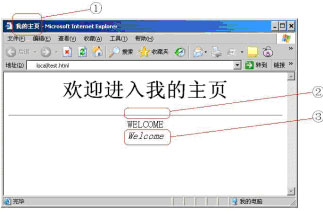
第 1 问
A. <TITLE>我的主页</TITLE>
B. <HEAD>我的主页</HEAD>
C. <BODY>我的主页</BODY>
D. <HI>我的主页</ HI >
第 2 问
A. <HR>
B. <LINE></LINE>
C. <CELL></CELL>
D. <TR></TR>
第 3 问
A. <B>Welcome</B>
B. <UL>Welcome</UL>
C. <I>Welcome</I>
D. <H>Welcome</H>
以下关于快速排序算法的描述中,错误的是( )。在快速排序过程中,需要设立基准元素并划分序列来进行排序。若序列由元素{12,25,30,45,52,67,85}构成,则初始排列为( )时,排序效率最高(令序列的第一个元素为基准元素)。
第 1 问
A. 快速排序算法是不稳定的排序算法
B. 快速排序算法在最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(nlgn)
C. 快速排序算法是一种分治算法
D. 当输入数据基本有序时,快速排序算法具有最坏情况下的时间复杂度
第 2 问
A. 45,12,30,25,67,52,85
B. 85,67,52,45,30,25,12
C. 12,25,30,45,52,67,85
D. 45,12,25,30,85,67,52
某算法的时间复杂度表达式为T(n)=an2+bnlgn+cn+d,其中,n为问题的规模,a、b、c和d为常数,用O表示其渐近时间复杂度为( )。
A. O(n2)
B. O(n)
C. O(nlgn)
D. O(1)
字符串采用链表存储方式时,每个结点存储多个字符有助于提高存储密度。若采用结点大小相同的链表存储串,则串比较、求子串、串连接、串替换等串的基本运算中,( )。
A. 进行串的比较运算最不方便
B. 进行求子串运算最不方便
C. 进行串连接最不方便
D. 进行串替换最不方便
对于长度为m (m>1)的指定序列,通过初始为空的一个栈、一个队列后,错误的叙述是( )。
A. 若入栈和入队的序列相同,则出栈序列和出队序列可能相同
B. 若入栈和入队的序列相同,则出栈序列和出队序列可以互为逆序
C. 入队序列与出队序列关系为1:1,而入栈序列与出栈序列关系是1 :n(n≥1)
D. 入栈序列与出栈序列关系为1:1,而入队序列与出队序列关系是1 :n(n≥1)
邻接矩阵和邻接表是图(网)的两种基本存储结构,对于具有n个顶点、e条边的图,( )。
A. 进行深度优先遍历运算所消耗的时间与采用哪一种存储结构无关
B. 进行广度优先遍历运算所消耗的时间与采用哪一种存储结构无关
C. 采用邻接表表示图时,查找所有顶点的邻接顶点的时间复杂度为O(n*e)
D. 采用邻接矩阵表示图时,查找所有顶点的邻接顶点的时间复杂度为O (n2)