若循环冗余校验码CRC的生成器为10111,则对于数据10100010000计算的校验码应为( )。该CRC校验码能够检测出的突发长度不超过( )。
第 1 问
A. 1101
B. 11011
C. 1001
D. 10011
第 2 问
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
The network layer provides services to the transport layer.It can be based on either( ). In both cases, its main job is ( )packets from the source to the destination.
In network layer, subnets can easily become congested, increasing the delay and ( )for packets.Network designers attempt to avoid congestion by proper design.Techniques include ( ) policy, caching, flow control, and more.
The next step beyond just dealing with congestion is to actually try to achieve a promisedquality of service.The methods that can be used for this include buffering at the client, trafficshaping, resource ( ), and admission control.Approaches that have been designed forgood quality of service include integrated services (including RSVP), differentiated services, and MPLS.
第 1 问
A. virtual circuits or datagrams
B. TCP or UDP
C. TCP or IP
D. IP or ARP
第 2 问
A. dealing with
B. routing
C. sending
D. receiving
第 3 问
A. lowering the throughput
B. lowering the correctness
C. lowering the effectiveness
D. lowering the preciseness
第 4 问
A. abandonment
B. retransmission
C. checksum
D. synchronism
第 5 问
A. distribution
B. guarantee
C. scheme
D. reservation
某公司新建一座200平米的厂房,现准备布置生产某产品的设备。该公司现空闲生产该产品的甲、乙、丙、丁四种型号的设备各3台,每种型号设备每天的生产能力由下表给出,在厂房大小限定的情况下,该厂房每天最多能生产该产品( )个。
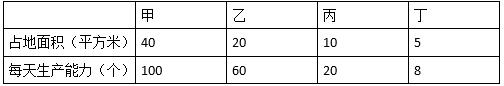
A. 500
B. 520
C. 524
D. 530
利用M/M/1排队论理论对分组交换和报文交换的平均延迟时间进行分析,其结果是( )。
A. 分组交换的平均延迟时间比报文交换的平均延时时间小
B. 分组交换的平均延迟时间比报文交换的平均延时时间大
C. 分组交换的平均延迟时间与报文交换的平均延时时间一样大
D. 要视网络的状态而定
项目成本控制是指( )。
A. 对成本费用的趋势及可能达到的水平所作的分析和推断
B. 预先规定计划期内项目施工的耗费和成本要达到的水平
C. 确定各个成本项目内比预计要达到的降低额和降低率
D. 在项目施工成本的形成过程中,对形成成本的要素进行监督,调节和控制
项目风险管理的工作流程是( )。
A. 风险辨识、风险分析、风险控制、风险转移
B. 风险辨识、风险分析、风险转移、风险控制
C. 风险辨识、风险转移、风险分析、风险控制
D. 风险转移、风险辨识、风险分析、风险控制
在项目的每一个阶段结束时,审查项目完成情况与可交付成果是( )。
A. 根据项目基线确定完成项目所需的资源数量
B. 根据已完成的工作量调整时间安排与成本基线
C. 决定项目是否应进入下一阶段
D. 接受客户对所交付项目的验收