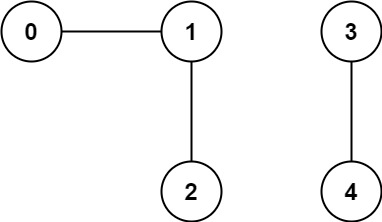
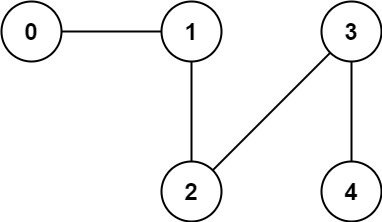
C++
Java
Python
Python3
C
C#
JavaScript
TypeScript
PHP
Swift
Kotlin
Dart
Go
Ruby
Scala
Rust
Racket
Erlang
Elixir
monokai
ambiance
chaos
chrome
cloud9_day
cloud9_night
cloud9_night_low_color
clouds
clouds_midnight
cobalt
crimson_editor
dawn
dracula
dreamweaver
eclipse
github
github_dark
gob
gruvbox
gruvbox_dark_hard
gruvbox_light_hard
idle_fingers
iplastic
katzenmilch
kr_theme
kuroir
merbivore
merbivore_soft
mono_industrial
nord_dark
one_dark
pastel_on_dark
solarized_dark
solarized_light
sqlserver
terminal
textmate
tomorrow
tomorrow_night
tomorrow_night_blue
tomorrow_night_bright
tomorrow_night_eighties
twilight
vibrant_ink
xcode
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
int countComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
}
};
运行代码
提交
golang 解法, 执行用时: 4 ms, 内存消耗: 4.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-21 23:11:45
func countComponents(n int, edges [][]int) int {
//无边那就快速直接返回顶点数作为答案(不写也行,下面也能统计出来)
if len(edges) == 0 {
return n
}
nodeColor := make([]int, n) //统计染色
color := 1
for _, pair := range edges {
if nodeColor[pair[0]] == 0 && nodeColor[pair[1]] == 0 {
nodeColor[pair[0]] = color
nodeColor[pair[1]] = color
color++
} else if nodeColor[pair[0]] != 0 && nodeColor[pair[1]] == 0 {
nodeColor[pair[1]] = nodeColor[pair[0]]
} else if nodeColor[pair[1]] != 0 && nodeColor[pair[0]] == 0 {
nodeColor[pair[0]] = nodeColor[pair[1]]
} else if nodeColor[pair[0]] != nodeColor[pair[1]] {
//链接的两端颜色不同的时候需要循环染成同一种颜色
fromColor := nodeColor[pair[0]]
toColor := nodeColor[pair[1]]
for i, _ := range nodeColor {
if nodeColor[i] == fromColor {
nodeColor[i] = toColor
}
}
}
}
p := make(map[int]int)
count := 0 //统计独立点
for _, v := range nodeColor {
if v == 0 {
count++
} else {
p[v] = 1
}
}
return len(p) + count //染色数 + 独立点数
}
golang 解法, 执行用时: 12 ms, 内存消耗: 5.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-21 23:11:17
func countComponents(n int, edges [][]int) int {
uf := NewUF(n, edges)
for i:=0; i<len(edges); i++ {
edge := edges[i]
if !uf.Connected(edge[0], edge[1]) {
uf.Union(edge[0], edge[1])
}
}
return uf.Count()
}
type UF struct {
parent map[int]int
size map[int]int
count int
}
func NewUF(n int, edges [][]int) *UF {
uf := UF{}
uf.parent = make(map[int]int, n)
uf.size = make(map[int]int, n)
uf.count = n
for i:=0; i<n; i++ {
uf.parent[i] = i
uf.size[i] = 1
}
return &uf
}
func (uf *UF) Find(a int) int {
for a != uf.parent[a] {
uf.parent[a] = uf.parent[uf.parent[a]]
a = uf.parent[a]
}
return a
}
func (uf *UF) Connected(a, b int) bool {
return uf.Find(a) == uf.Find(b)
}
func (uf *UF) Union(a, b int) {
pA := uf.Find(a)
pB := uf.Find(b)
if uf.size[pA] > uf.size[pB] {
uf.parent[pB] = pA
uf.size[pA] += uf.size[pB]
} else {
uf.parent[pA] = pB
uf.size[pB] += uf.size[pA]
}
uf.count--
}
func (uf *UF) Count() int {
return uf.count
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 52 ms, 内存消耗: 18.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-21 23:10:53
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
self.part = n
self.parent = [x for x in range(n)]
self.size = [1 for _ in range(n)]
######## 只有扁平化,路径压缩
def Find(self, x: int) -> int:
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.Find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def Union(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
root_x = self.Find(x)
root_y = self.Find(y)
if root_x == root_y:
return False
self.parent[root_x] = root_y
self.size[root_y] += self.size[root_x]
self.part -= 1
return True
def in_the_same_part(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
return self.Find(x) == self.Find(y)
def get_part_size(self, x: int) -> int:
root_x = self.Find(x)
return self.size[root_x]
class Solution:
def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
UF = UnionFind(n)
for x, y in edges:
UF.Union(x, y)
return UF.part
python3 解法, 执行用时: 52 ms, 内存消耗: 17.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-21 23:10:19
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
self.part = n
self.parent = [x for x in range(n)]
self.size = [1 for _ in range(n)]
def Find(self, x: int) -> int:
if self.parent[x] == x:
return x
return self.Find(self.parent[x])
def Union(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
root_x = self.Find(x)
root_y = self.Find(y)
if root_x == root_y:
return False
if self.size[root_x] > self.size[root_y]:
root_x, root_y = root_y, root_x
self.parent[root_x] = root_y
self.size[root_y] += self.size[root_x]
self.part -= 1
return True
def in_the_same_part(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
return self.Find(x) == self.Find(y)
def get_part_size(self, x: int) -> int:
root_x = self.Find(x)
return self.size[root_x]
class Solution:
def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
UF = UnionFind(n)
for x, y in edges:
UF.Union(x, y)
return UF.part
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 40 ms, 内存消耗: 31.1 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-21 23:09:56
class Solution1 {
public:
int countComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
// Construct adjacent graph
vector<unordered_set<int>> graph(n);
visited = vector<bool>(n, false);
for (const auto& e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].insert(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].insert(e[0]);
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
count++;
dfs(graph, i);
}
}
return count;
}
// C++ UnionFind Utility class
private:
vector<bool> visited;
void dfs(vector<unordered_set<int>>& graph, int src) {
if (visited[src]) {
return;
}
visited[src] = true;
for (const auto& neighbor : graph[src]) {
dfs(graph, neighbor);
}
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int countComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
// Construct adjacent graph
vector<unordered_set<int>> graph(n);
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
for (const auto& e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].insert(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].insert(e[0]);
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue<int> q{{i}};
if (!visited[i]) {
count++;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto cur = q.front(); q.pop();
if (visited[cur]) {
continue;
}
visited[cur] = true;
for (const auto& neighbor : graph[cur]) {
q.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
class Solution3 {
public:
int countComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
UnionFind uf(n);
for (const auto& e : edges) {
auto pu = uf.find(e[0]);
auto pv = uf.find(e[1]);
if (pu != pv) {
uf.unite(pu, pv);
}
}
return uf.count();
}
// C++ UnionFind Utility class
private:
class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
parent = vector<int>(n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
int count() {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < parent.size(); i++) {
res += (i == parent[i]);
}
return res;
}
void unite(int px, int py) {
parent[px] = py;
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == parent[x]) {
return x;
}
return find(parent[x]);
}
private:
vector<int> parent;
};
};
java 解法, 执行用时: 4 ms, 内存消耗: 42.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-21 23:08:40
class Solution {
// 并查集
public int countComponents(int n, int[][] edges) {
int[] parents = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parents, -1);
for (int[] e : edges) {
int root1 = find(parents, e[0]);
int root2 = find(parents, e[1]);
if (root1 != root2) {
parents[root1] = root2;
n--;
}
}
return n;
}
private int find(int[] parents, int x) {
int root = x;
while (parents[root] != -1) root = parents[root];
return root;
}
// dfs
public int countComponents2(int n, int[][] edges) {
int count = 0;
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] edge : edges) {
adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
count++;
dfs(visited, i, adjList);
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(boolean[] visited, int index, List<List<Integer>> adjList) {
visited[index] = true;
for (int i : adjList.get(index)) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(visited, i, adjList);
}
}
}
// bfs
public int countComponents3(int n, int[][] edges) {
int count = 0;
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] edge : edges) {
adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
count++;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int index = queue.poll();
visited[index] = true;
for (int next : adjList.get(index)) {
if (!visited[next]) queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
}