class Robot {
public:
Robot(int width, int height) {
}
void step(int num) {
}
vector<int> getPos() {
}
string getDir() {
}
};
/**
* Your Robot object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Robot* obj = new Robot(width, height);
* obj->step(num);
* vector<int> param_2 = obj->getPos();
* string param_3 = obj->getDir();
*/
2069. 模拟行走机器人 II
给你一个在 XY 平面上的 width x height 的网格图,左下角 的格子为 (0, 0) ,右上角 的格子为 (width - 1, height - 1) 。网格图中相邻格子为四个基本方向之一("North","East","South" 和 "West")。一个机器人 初始 在格子 (0, 0) ,方向为 "East" 。
机器人可以根据指令移动指定的 步数 。每一步,它可以执行以下操作。
- 沿着当前方向尝试 往前一步 。
- 如果机器人下一步将到达的格子 超出了边界 ,机器人会 逆时针 转 90 度,然后再尝试往前一步。
如果机器人完成了指令要求的移动步数,它将停止移动并等待下一个指令。
请你实现 Robot 类:
Robot(int width, int height)初始化一个width x height的网格图,机器人初始在(0, 0),方向朝"East"。void move(int num)给机器人下达前进num步的指令。int[] getPos()返回机器人当前所处的格子位置,用一个长度为 2 的数组[x, y]表示。String getDir()返回当前机器人的朝向,为"North","East","South"或者"West"。
示例 1:
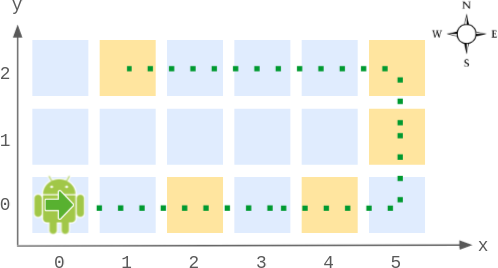
输入:
["Robot", "move", "move", "getPos", "getDir", "move", "move", "move", "getPos", "getDir"]
[[6, 3], [2], [2], [], [], [2], [1], [4], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, [4, 0], "East", null, null, null, [1, 2], "West"]
解释:
Robot robot = new Robot(6, 3); // 初始化网格图,机器人在 (0, 0) ,朝东。
robot.move(2); // 机器人朝东移动 2 步,到达 (2, 0) ,并朝东。
robot.move(2); // 机器人朝东移动 2 步,到达 (4, 0) ,并朝东。
robot.getPos(); // 返回 [4, 0]
robot.getDir(); // 返回 "East"
robot.move(2); // 朝东移动 1 步到达 (5, 0) ,并朝东。
// 下一步继续往东移动将出界,所以逆时针转变方向朝北。
// 然后,往北移动 1 步到达 (5, 1) ,并朝北。
robot.move(1); // 朝北移动 1 步到达 (5, 2) ,并朝 北 (不是朝西)。
robot.move(4); // 下一步继续往北移动将出界,所以逆时针转变方向朝西。
// 然后,移动 4 步到 (1, 2) ,并朝西。
robot.getPos(); // 返回 [1, 2]
robot.getDir(); // 返回 "West"
提示:
2 <= width, height <= 1001 <= num <= 105move,getPos和getDir总共 调用次数不超过104次。
原站题解