C++
Java
Python
Python3
C
C#
JavaScript
Ruby
Swift
Go
Scala
Kotlin
Rust
PHP
TypeScript
Racket
Erlang
Elixir
Dart
monokai
ambiance
chaos
chrome
cloud9_day
cloud9_night
cloud9_night_low_color
clouds
clouds_midnight
cobalt
crimson_editor
dawn
dracula
dreamweaver
eclipse
github
github_dark
gob
gruvbox
gruvbox_dark_hard
gruvbox_light_hard
idle_fingers
iplastic
katzenmilch
kr_theme
kuroir
merbivore
merbivore_soft
mono_industrial
nord_dark
one_dark
pastel_on_dark
solarized_dark
solarized_light
sqlserver
terminal
textmate
tomorrow
tomorrow_night
tomorrow_night_blue
tomorrow_night_bright
tomorrow_night_eighties
twilight
vibrant_ink
xcode
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
bool isPrintable(vector<vector<int>>& targetGrid) {
}
};
运行代码
提交
python3 解法, 执行用时: 500 ms, 内存消耗: 16.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-23 17:11:33
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def isPrintable(self, targetGrid: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
def build(c, inds):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = m, n, -1, -1
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if c == targetGrid[i][j]:
x1, y1 = min(x1, i), min(y1, j)
x2, y2 = max(x2, i), max(y2, j)
if x2 == -1: return
visited = [False] * N
for i in range(x1, x2 + 1):
for j in range(y1, y2+1):
tc = targetGrid[i][j]
if tc != c and not visited[tc]:
visited[tc] = True
inds[tc] += 1
g[c].append(tc)
N, m, n = 61, len(targetGrid), len(targetGrid[0])
g, inds = [[] for _ in range(N)], [0] * N
for i in range(0, N):
build(i, inds)
tot, q = 0, deque([i for i in range(N) if inds[i] == 0])
while q:
c = q.popleft()
tot += 1
for nc in g[c]:
inds[nc] -= 1
if inds[nc] == 0:
q.append(nc)
return tot == N
golang 解法, 执行用时: 32 ms, 内存消耗: 6.5 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-23 17:11:05
func isPrintable(targetGrid [][]int) bool {
// colors: 每个颜色的左上角坐标和右下角坐标
colors := make(map[int][]int)
for i := 0; i < len(targetGrid); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(targetGrid[i]); j ++ {
if pos, ok := colors[targetGrid[i][j]]; ok {
pos[0] = min(i, pos[0])
pos[1] = min(j, pos[1])
pos[2] = max(i, pos[2])
pos[3] = max(j, pos[3])
} else {
colors[targetGrid[i][j]] = []int{i, j, i, j}
}
}
}
// 检查颜色color是否构成矩形
check := func(color int) bool {
pos := colors[color]
for i := pos[0]; i <= pos[2]; i++ {
for j := pos[1]; j <= pos[3]; j++ {
if targetGrid[i][j] != color && targetGrid[i][j] != 0 {
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
// 把颜色为color的块置0
mark := func(color int) {
for i := 0; i < len(targetGrid); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(targetGrid[i]); j ++ {
if targetGrid[i][j] == color {
targetGrid[i][j] = 0
}
}
}
}
// 对每种颜色,检查是否是矩形,是则把相应块置0并删除该颜色
keepGoing := true
for keepGoing {
keepGoing = false
for color, _ := range colors {
if check(color) {
mark(color)
delete(colors, color)
keepGoing = true
break
}
}
}
// 检查是否剩余颜色
return len(colors) == 0
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
golang 解法, 执行用时: 336 ms, 内存消耗: 7.5 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-23 17:10:53
var rLength, cLength int
type RectArea struct {
RowScope *Scope
ColScope *Scope
}
// IsInArae 是否落在该区域内
func (ra *RectArea) IsInArae(r, c int) bool {
if r >= ra.RowScope.Min && r <= ra.RowScope.Max &&
c >= ra.ColScope.Min && c <= ra.ColScope.Max {
return true
}
return false
}
type Scope struct {
Min int
Max int
}
// Update 更新区域的Min和Max
func (s *Scope) Update(v int) {
if v < s.Min {
s.Min = v
}
if v > s.Max {
s.Max = v
}
}
/**
题目出处:https://leetcode.cn/problems/strange-printer-ii/
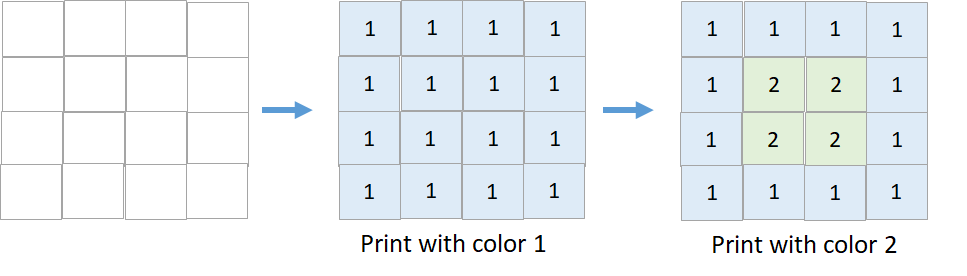
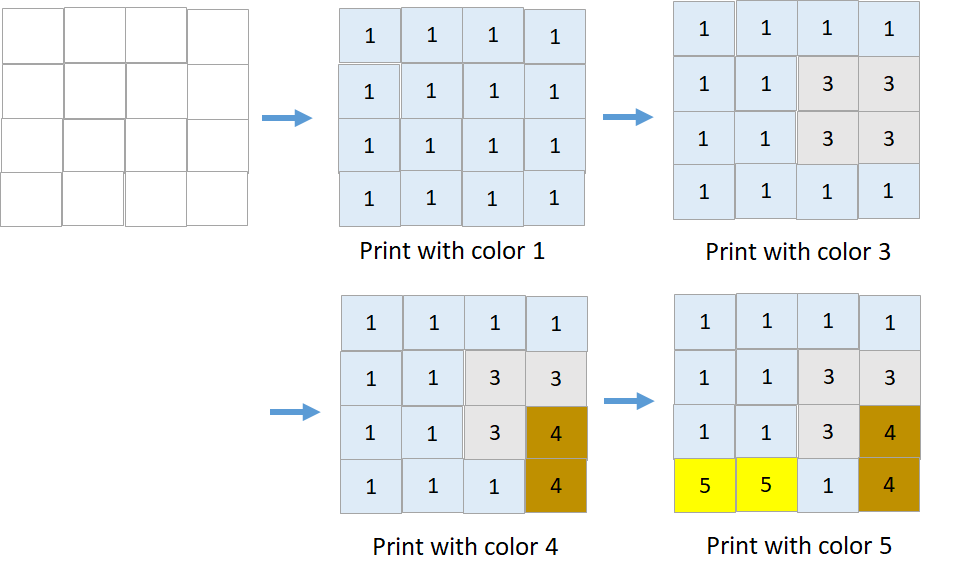
思路:如下的case
6 2 2 5
2 2 2 5
2 2 2 5
4 3 3 4
涂色问题其实就是一个拓扑排序,如:打印颜色6必须先打印颜色2,因此判断是否能打印,最根本就是需要DAG是否存在环
1. 从图中提取出DAG拓扑图,如颜色6落入了2矩阵中,因此打印颜色6需要先打印颜色2
2. 初始化入度表和邻接矩阵
3. 最后判断DAG是否存在环即可
3.1、获取入度表中入度为0的节点进行遍历
3.2、遍历入度为0的节点:将该节点设置为-1(已遍历),子节点对应的入度-1,重复3.1,直到没有入度为0的节点为止
*/
func isPrintable(targetGrid [][]int) bool {
indegrees, adjMat := initParams(targetGrid)
nodes := getRootNode(indegrees)
for len(nodes) != 0 {
for _, c := range nodes {
indegrees[c] = -1000
columns := adjMat[c]
for col, v := range columns {
if col == c {
continue
}
if v == 1 {
indegrees[col] -= 1
}
}
}
nodes = getRootNode(indegrees)
}
for _, num := range indegrees {
if num > 0 {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func getRootNode(indegrees map[int]int) []int {
var res []int
for c, indegreNum := range indegrees {
if indegreNum == 0 {
res = append(res, c)
}
}
return res
}
func findArea(r, col, c int, colorRectAreaMap map[int]*RectArea) map[int]bool {
areas := make(map[int]bool)
for color, area := range colorRectAreaMap {
if c == color {
continue
}
if area.IsInArae(r, col) {
areas[color] = true
}
}
return areas
}
func initParams(targetGrid [][]int) (map[int]int, [][]int) {
colorRectAreaMap := make(map[int]*RectArea)
indegrees := make(map[int]int)
tmpIndegrees := make(map[int]map[int]bool)
var adjMat [][]int
for rIndex, columns := range targetGrid {
for cIndex, color := range columns {
indegrees[color] = 0
tmpIndegrees[color] = make(map[int]bool)
area, ok := colorRectAreaMap[color]
if !ok {
colorRectAreaMap[color] = &RectArea{
RowScope: &Scope{Min: rIndex, Max: rIndex},
ColScope: &Scope{Min: cIndex, Max: cIndex},
}
continue
}
area.RowScope.Update(rIndex)
area.ColScope.Update(cIndex)
}
}
// init adjMap
maxColor := MaxColor(indegrees) + 1
adjMat = make([][]int, maxColor)
for rIndex, _ := range adjMat {
adjMat[rIndex] = make([]int, maxColor)
}
for rIndex, columns := range targetGrid {
for cIndex, color := range columns {
areas := findArea(rIndex, cIndex, color, colorRectAreaMap)
tmpIndegrees[color] = union(tmpIndegrees[color], areas)
for area, _ := range areas {
adjMat[area][color] = 1
}
}
}
for color, areaMap := range tmpIndegrees {
indegrees[color] = len(areaMap)
}
return indegrees, adjMat
}
func union(a map[int]bool, b map[int]bool) map[int]bool {
for v, _ := range a {
b[v] = true
}
return b
}
func MaxColor(indegrees map[int]int) int {
maxColor := 0
for c, _ := range indegrees {
if c > maxColor {
maxColor = c
}
}
return maxColor
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 460 ms, 内存消耗: 30.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-23 17:10:20
class Solution:
def isPrintable(self, targetGrid: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
colors = collections.defaultdict(set) # 【同种颜色格子坐标集合】
for r,row in enumerate(targetGrid):
for c,pt in enumerate(row):
colors[pt].add((r,c))
scale = {p : [
min(r for r,c in colors[p]),
min(c for r,c in colors[p]),
max(r for r,c in colors[p]),
max(c for r,c in colors[p])]
for p in colors
} # 【覆盖某颜色所需的最小矩形】
unfilled = {p: set(
(r,c)
for r in range(scale[p][0],scale[p][2]+1)
for c in range(scale[p][1],scale[p][3]+1)
if targetGrid[r][c]!=p
)
for p in colors
} #【某颜色的最小矩形中,不是该颜色的格子坐标集合】
while(unfilled):
for p in unfilled:
if not unfilled[p]: # 选取一个可以上色的颜色;
break
else:
return False # 如果没有,则说明没有合适的方案,返回false;
unfilled.pop(p)
for q in unfilled:
unfilled[q]-=colors[p] # 上色的过程,去掉其他所有元素的unfilled
return True
java 解法, 执行用时: 27 ms, 内存消耗: 42.6 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-23 17:09:47
class Solution {
public boolean isPrintable(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length, maxv = 60;
int[][] colorArea = new int[maxv + 1][]; //总共有不超过 60 种颜色,且颜色编号从 0 开始,colorArea[c] 代表颜色 c 的范围,按照上下左右的顺序给出
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int c = grid[i][j];
if(colorArea[c] == null) colorArea[c] = new int[]{i, i, j, j}; // 上下左右
else {
int a[] = colorArea[c];
a[1] = i;
a[2] = Math.min(j, a[2]);
a[3] = Math.max(j, a[3]);
}
}
}
// 建立邻接表、入度表,节点 v 出现在 colorArea[u] 范围里,则记录一条 u 到 v 的有向边。注意,边可能是双向的。
List<Integer>[] adt = new List[maxv + 1];
int[] inDegree = new int[maxv + 1];
boolean[][] handled = new boolean[maxv + 1][maxv + 1];
for(int i = 0; i <= maxv; i++) adt[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int v = grid[i][j];
for(int u = 1; u <= maxv; u++){
int[] a = colorArea[u];
if(u == v || a == null || handled[u][v])continue;
if(i >= a[0] && i <= a[1] && j >= a[2] && j <= a[3]){
adt[u].add(v);
inDegree[v]++;
handled[u][v] = true;
}
}
}
}
// 拓扑排序
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 1; i <= maxv; i++){
if(inDegree[i] == 0)queue.offer(i);
}
int left = maxv;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int u = queue.poll();
left--;
for(int v: adt[u]){
if(--inDegree[v] == 0)queue.offer(v);
}
}
return left == 0;
}
}
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 76 ms, 内存消耗: 15.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-23 17:09:20
class Solution {
public:
bool isPrintable(vector<vector<int>>& t) {
int i,j,k,m,n;
m=t.size();
n=t[0].size();
int top[61],bottom[61],left[61],right[61];
memset(top,0x3f,sizeof(top));
memset(bottom,0xff,sizeof(bottom));
memset(left,0x3f,sizeof(left));
memset(right,0xff,sizeof(right));
//对每种颜色的顶、底、左、右边界进行初始化
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
k=t[i][j];
top[k]=min(top[k],i);
bottom[k]=max(bottom[k],i);
left[k]=min(left[k],j);
right[k]=max(right[k],j);
}
}
//遍历矩阵,获取每种颜色的上下左右边界
bool haveedge[61][61]={0};
//haveedge用于避免重复建边
vector<int>edgefrom[61];
//edgefrom[i]表示从i出发的有向边
int deg[61]={0};
//deg[i]表示颜色i的入度
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
//用i,j做下标遍历图中每个像素
k=t[i][j];
for(int color=1;color<=60;color++){
if(top[color]<=i&&i<=bottom[color]&&left[color]<=j&&j<=right[color]){
if(color!=k&&!haveedge[color][k]){
edgefrom[color].push_back(k);
deg[k]++;
haveedge[color][k]=true;
}
}
//若t[i][j]位于颜色为color的矩形内部,颜色却不为color为k
//说明先染成color,再染成k
//建立有向边color → k
}
}
}
vector<int>v;
while(true){
for(i=1;i<=60;i++){
if(deg[i]==0){
v.push_back(i);
deg[i]=-1;
for(int a:edgefrom[i]){
deg[a]--;
}
break;
}
}
if(i==61)break;
}
//将入度为0的颜色放入v,最后看1~60是不是都能放入v
return v.size()==60;
}
};