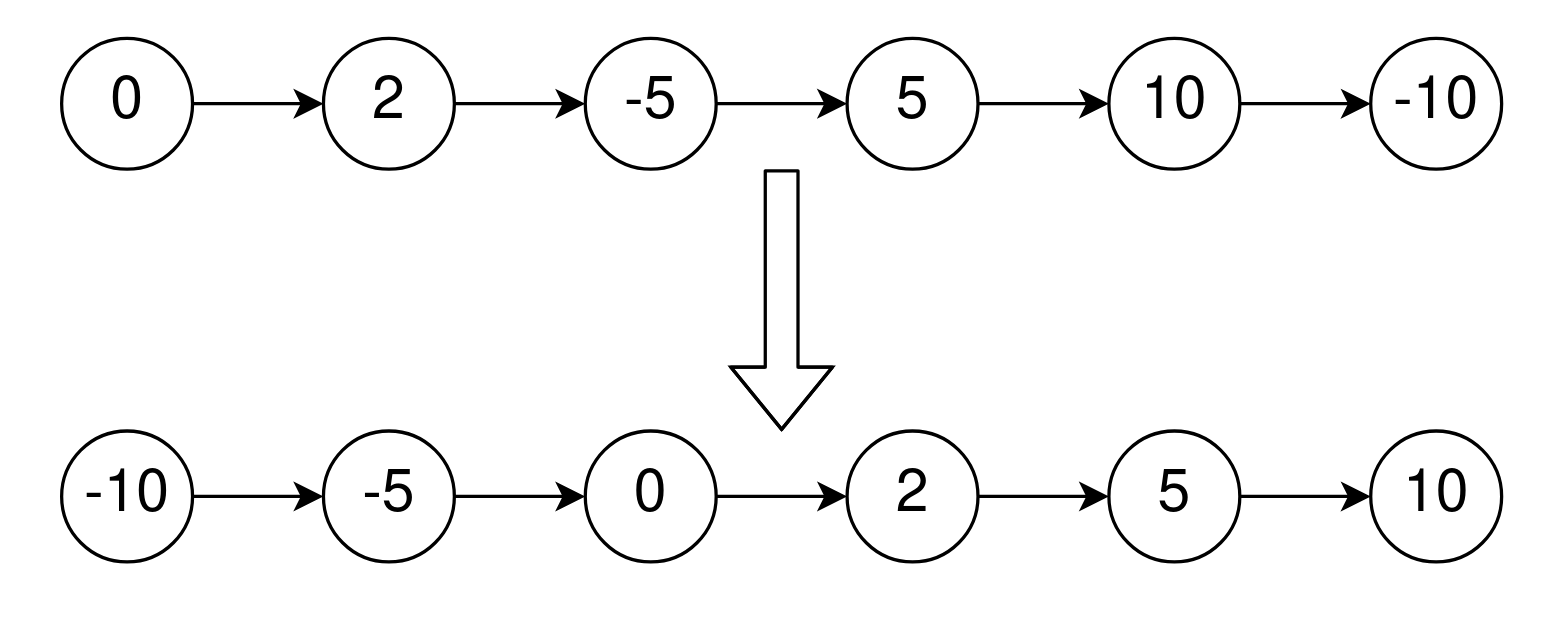
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortLinkedList(ListNode* head) {
}
};
java 解法, 执行用时: 53 ms, 内存消耗: 61 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-17 16:58:47
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
// 最小堆
class Solution {
public ListNode sortLinkedList(ListNode head) {
PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)-> a.val - b.val);
ListNode p = head, dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
while (p!=null){
pq.add(p);
p = p.next;
}
p = dummy;
while (!pq.isEmpty()){
p.next = pq.poll();
p = p.next;
}
p.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
}
java 解法, 执行用时: 2 ms, 内存消耗: 60 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-17 16:58:07
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortLinkedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = head, curr = head.next;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.val < 0) {
ListNode t = curr.next;
prev.next = t;
curr.next = head;
head = curr;
curr = t;
} else {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 184 ms, 内存消耗: 90.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-17 16:57:35
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortLinkedList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = head;
ListNode* curr = head->next;
while (curr)
{
if (curr->val < 0)
{
auto t = curr->next;
prev->next = t;
curr->next = head;
head = curr;
curr = t;
}
else
{
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
golang 解法, 执行用时: 80 ms, 内存消耗: 8.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-17 16:57:15
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func sortLinkedList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
prev, curr := head, head.Next
for curr != nil {
if curr.Val < 0 {
t := curr.Next
prev.Next = t
curr.Next = head
head = curr
curr = t
} else {
prev, curr = curr, curr.Next
}
}
return head
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 332 ms, 内存消耗: 58.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-10-17 16:57:00
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
'''
头插法,默认第一个节点已经排好序,从第二个点开始,遇到负数,头插法,非负继续往下
'''
class Solution:
def sortLinkedList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
prev, curr = head, head.next
while curr:
if curr.val < 0:
t = curr.next
prev.next = t
curr.next = head
head = curr
curr = t
else:
prev, curr = curr, curr.next
return head