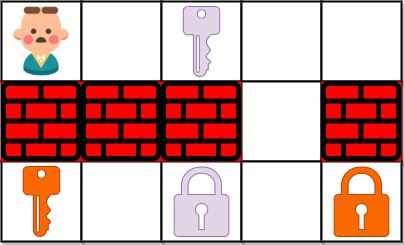
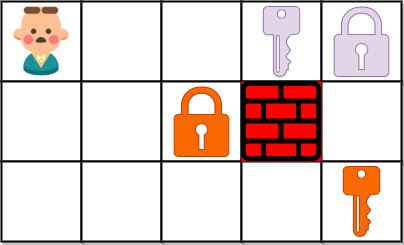
python3 解法, 执行用时: 296 ms, 内存消耗: 20.2 MB, 提交时间: 2022-11-10 16:35:35
class Solution:
def shortestPathAllKeys(self, g: List[str]) -> int:
dirs = [[0,1], [0,-1], [1,0], [-1,0]]
n, m, cnt = len(g), len(g[0]), 0
dist = defaultdict(lambda : 0x3f3f3f3f)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
c = g[i][j]
if c == '@':
d = deque([(i, j, 0)])
dist[(i, j, 0)] = 0
elif 'a' <= c <= 'z':
cnt += 1
while d:
x, y, cur = d.popleft()
step = dist[(x, y, cur)]
for di in dirs:
nx, ny = x + di[0], y + di[1]
if nx < 0 or nx >= n or ny < 0 or ny >= m:
continue
c = g[nx][ny]
if c == '#':
continue
if 'A' <= c <= 'Z' and (cur >> (ord(c) - ord('A')) & 1) == 0:
continue
ncur = cur
if 'a' <= c <= 'z':
ncur |= (1 << (ord(c) - ord('a')))
if ncur == (1 << cnt) - 1:
return step + 1
if step + 1 >= dist[(nx, ny, ncur)]:
continue
dist[(nx, ny, ncur)] = step + 1
d.append((nx, ny, ncur))
return -1
python3 解法, 执行用时: 228 ms, 内存消耗: 20.1 MB, 提交时间: 2022-11-10 16:29:35
class Solution:
def shortestPathAllKeys(self, grid: List[str]) -> int:
dirs = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)] # 左、右、下、上
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
sx = sy = 0
key_to_idx = dict()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == "@": # 人初始位置
sx, sy = i, j
elif grid[i][j].islower():
if grid[i][j] not in key_to_idx:
idx = len(key_to_idx)
key_to_idx[grid[i][j]] = idx
q = deque([(sx, sy, 0)])
dist = dict()
dist[(sx, sy, 0)] = 0
while q:
x, y, mask = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] != "#":
if grid[nx][ny] == "." or grid[nx][ny] == "@":
if (nx, ny, mask) not in dist:
dist[(nx, ny, mask)] = dist[(x, y, mask)] + 1
q.append((nx, ny, mask))
elif grid[nx][ny].islower():
idx = key_to_idx[grid[nx][ny]]
if (nx, ny, mask | (1 << idx)) not in dist:
dist[(nx, ny, mask | (1 << idx))] = dist[(x, y, mask)] + 1
if (mask | (1 << idx)) == (1 << len(key_to_idx)) - 1:
return dist[(nx, ny, mask | (1 << idx))]
q.append((nx, ny, mask | (1 << idx)))
else:
idx = key_to_idx[grid[nx][ny].lower()]
if (mask & (1 << idx)) and (nx, ny, mask) not in dist:
dist[(nx, ny, mask)] = dist[(x, y, mask)] + 1
q.append((nx, ny, mask))
return -1