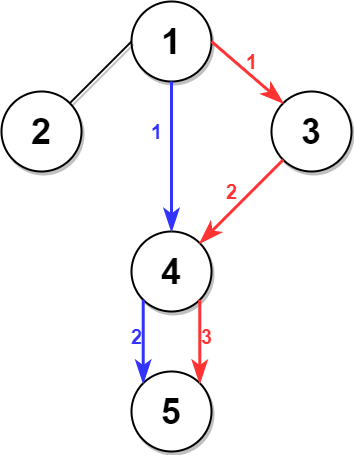
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
int secondMinimum(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int time, int change) {
}
};
golang 解法, 执行用时: 332 ms, 内存消耗: 8.7 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-17 12:08:24
const inf int = 0x3f3f3f3f
func secondMinimum(n int, edges [][]int, time int, change int) (ans int) {
graph := map[int][]int{}
for _, edge := range edges{
graph[edge[0] - 1] = append(graph[edge[0] - 1], edge[1] - 1)
graph[edge[1] - 1] = append(graph[edge[1] - 1], edge[0] - 1)
}
explored := make([][]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++{
explored[i] = []int{inf, inf}
}
explored[0][0] = 0
queue := [][]int{{0, 0}}
out:
for len(queue) > 0{
idx, dist := queue[0][0], queue[0][1]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, other := range graph[idx]{
if explored[other][0] > dist + 1{
explored[other][0] = dist + 1
} else if explored[other][0] < dist + 1 && explored[other][1] > dist + 1{
explored[other][1] = dist + 1
if other == n - 1{
break out
}
} else{
continue
}
queue = append(queue, []int{other, dist + 1})
}
}
for i := 0; i < explored[n - 1][1]; i++ {
ans += time
if i < explored[n-1][1] - 1 && (ans / change) % 2 == 1{
ans = (ans + change)/change * change
}
}
return
}
javascript 解法, 执行用时: 256 ms, 内存消耗: 66.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-17 12:08:00
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @param {number} time
* @param {number} change
* @return {number}
*/
const INF = 0x3f3f3f3f
var secondMinimum = function(n, edges, time, change) {
const graph = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array());
for (const edge of edges) {
graph[edge[0] - 1].push(edge[1] - 1);
graph[edge[1] - 1].push(edge[0] - 1);
}
const explored = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(2).fill(INF))
let queue = [0], dist = 0
out:
while(queue.length > 0){
dist += 1
const nxt = new Array()
for(const idx of queue)
for(const other of graph[idx]){
if(explored[other][0] > dist)
explored[other][0] = dist
else if(explored[other][0] < dist && explored[other][1] > dist){
explored[other][1] = dist
if(other == n - 1)
break out
}
else
continue
nxt.push(other)
}
queue = nxt
}
let ans = 0
for(let i = 0; i < explored[n-1][1]; i++){
ans += time
if(i < explored[n-1][1] -1 && Math.floor(ans/change) % 2 == 1)
ans = Math.floor((ans + change)/change) * change
}
return ans
};
java 解法, 执行用时: 81 ms, 内存消耗: 54.5 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-17 12:07:43
class Solution {
private static final int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
public int secondMinimum(int n, int[][] edges, int time, int change) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] edge: edges){
List<Integer> a = graph.getOrDefault(edge[0] - 1, new ArrayList<>());
List<Integer> b = graph.getOrDefault(edge[1] - 1, new ArrayList<>());
a.add(edge[1] - 1);
b.add(edge[0] - 1);
graph.put(edge[0] - 1, a);
graph.put(edge[1] - 1, b);
}
int[][] explored = new int[n][2];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
Arrays.fill(explored[i], INF);
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.addLast(new int[]{0, 0});
explored[0][0] = 0;
out:
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = queue.pollFirst();
int idx = cur[0], nxtDist = cur[1] + 1;
for(int other: graph.get(idx)){
if(nxtDist < explored[other][0])
explored[other][0] = nxtDist;
else if(nxtDist > explored[other][0] && nxtDist < explored[other][1]){
explored[other][1] = nxtDist;
if(other == n - 1)
break out;
}
else
continue;
queue.addLast(new int[]{other, nxtDist});
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<explored[n-1][1];i++){
ans += time;
if(i < explored[n-1][1] - 1 && (ans / change) % 2 == 1)
ans = (ans + change) / change * change;
}
return ans;
}
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 504 ms, 内存消耗: 27 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-17 12:07:29
'''
由于time和change是固定的,而不是在不同边有不同的值,
所以我们可以统计出起点到终点的最短距离和次短距离,然后根据次短距离计算答案。
'''
class Solution:
def secondMinimum(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], time: int, change: int) -> int:
graph = defaultdict(set)
for a,b in edges:
graph[a].add(b)
graph[b].add(a)
# idx, dist
pq = deque([(1, 0)])
explored = [[inf] * 2 for _ in range(n)]
explored[0][0] = 0
while pq:
idx, dist = pq.popleft()
for other in graph[idx]:
if dist + 1 < explored[other - 1][0]:
explored[other - 1][0] = dist + 1
elif explored[other - 1][0] < dist + 1 < explored[other - 1][1]:
explored[other - 1][1] = dist + 1
if other == n:
ans = 0
for i in range(explored[-1][1]):
ans += time
if i < explored[-1][1] - 1 and (ans // change) % 2:
ans = (ans + change) // change * change
return ans
else:
continue
pq.append((other, dist + 1))
return -1
golang 解法, 执行用时: 268 ms, 内存消耗: 9.5 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-17 12:06:47
/**
* 简单说一下为什么可以用 BFS。由于 time\ 和 change 是固定的,
* 经过多少条边就知道花费了多少时间。因此这题本质上可以看成边权均为 1 的图,
* 我们要求的就是 1 到 n 的严格次短路的长度,知道长度就知道花费的时间。
* 下面的代码是直接用 BFS 求次短时间。
*/
func secondMinimum(n int, edges [][]int, time, change int) int {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges { // 建图
v, w := e[0]-1, e[1]-1
g[v] = append(g[v], w)
g[w] = append(g[w], v)
}
// 传入当前时间 d,返回到达下一个节点的时间
next := func(d int) int {
if times := d / change; times%2 == 1 { // 如果红绿灯切换次数为奇数,则现在是红灯
return (times+1)*change + time // 等绿灯再出发
}
return d + time // 绿灯,直接出发
}
dis := make([][2]int, n) // 距离数组同时存 [最短路, 次短路]
dis[0][1] = 1e9
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
dis[i] = [2]int{1e9, 1e9}
}
type pair struct{ v, d int }
q := []pair{{}}
for len(q) > 0 { // BFS 求最短路和次短路
p := q[0] // 取队首
q = q[1:]
for _, w := range g[p.v] {
d := next(p.d) // 到达节点 w 的时间
if d < dis[w][0] { // d 比最短路小,就更新最短路
dis[w][0] = d
q = append(q, pair{w, d})
} else if dis[w][0] < d && d < dis[w][1] { // d 比最短路大又比次短路小,就更新次短路
dis[w][1] = d
q = append(q, pair{w, d})
}
}
}
return dis[n-1][1]
}