C++
Java
Python
Python3
C
C#
JavaScript
Ruby
Swift
Go
Scala
Kotlin
Rust
PHP
TypeScript
Racket
Erlang
Elixir
Dart
monokai
ambiance
chaos
chrome
cloud9_day
cloud9_night
cloud9_night_low_color
clouds
clouds_midnight
cobalt
crimson_editor
dawn
dracula
dreamweaver
eclipse
github
github_dark
gob
gruvbox
gruvbox_dark_hard
gruvbox_light_hard
idle_fingers
iplastic
katzenmilch
kr_theme
kuroir
merbivore
merbivore_soft
mono_industrial
nord_dark
one_dark
pastel_on_dark
solarized_dark
solarized_light
sqlserver
terminal
textmate
tomorrow
tomorrow_night
tomorrow_night_blue
tomorrow_night_bright
tomorrow_night_eighties
twilight
vibrant_ink
xcode
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class NumMatrix {
public:
NumMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
}
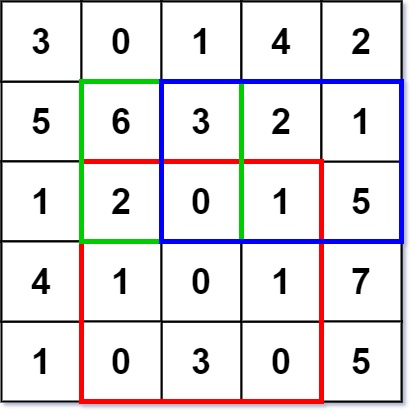
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
}
};
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumMatrix* obj = new NumMatrix(matrix);
* int param_1 = obj->sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
运行代码
提交
golang 解法, 执行用时: 560 ms, 内存消耗: 16.5 MB, 提交时间: 2022-11-23 11:46:24
type NumMatrix struct {
sums [][]int
}
func Constructor(matrix [][]int) NumMatrix {
sums := make([][]int, len(matrix))
for i, row := range matrix {
sums[i] = make([]int, len(row)+1)
for j, v := range row {
sums[i][j+1] = sums[i][j] + v
}
}
return NumMatrix{sums}
}
func (nm *NumMatrix) SumRegion(row1, col1, row2, col2 int) (sum int) {
for i := row1; i <= row2; i++ {
sum += nm.sums[i][col2+1] - nm.sums[i][col1]
}
return
}
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(matrix);
* param_1 := obj.SumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
golang 解法, 执行用时: 532 ms, 内存消耗: 16.5 MB, 提交时间: 2022-11-23 11:46:06
type NumMatrix struct {
sums [][]int
}
func Constructor(matrix [][]int) NumMatrix {
m := len(matrix)
if m == 0 {
return NumMatrix{}
}
n := len(matrix[0])
sums := make([][]int, m+1)
sums[0] = make([]int, n+1)
for i, row := range matrix {
sums[i+1] = make([]int, n+1)
for j, v := range row {
sums[i+1][j+1] = sums[i+1][j] + sums[i][j+1] - sums[i][j] + v
}
}
return NumMatrix{sums}
}
func (nm *NumMatrix) SumRegion(row1, col1, row2, col2 int) int {
return nm.sums[row2+1][col2+1] - nm.sums[row1][col2+1] - nm.sums[row2+1][col1] + nm.sums[row1][col1]
}
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(matrix);
* param_1 := obj.SumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
python3 解法, 执行用时: 556 ms, 内存消耗: 25.7 MB, 提交时间: 2022-11-23 11:44:24
class NumMatrix:
'''
二维前缀和
'''
def __init__(self, matrix: List[List[int]]):
m, n = len(matrix), (len(matrix[0]) if matrix else 0)
self.sums = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
_sums = self.sums
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
_sums[i + 1][j + 1] = _sums[i][j + 1] + _sums[i + 1][j] - _sums[i][j] + matrix[i][j]
def sumRegion(self, row1: int, col1: int, row2: int, col2: int) -> int:
_sums = self.sums
return _sums[row2 + 1][col2 + 1] - _sums[row1][col2 + 1] - _sums[row2 + 1][col1] + _sums[row1][col1]
# Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumMatrix(matrix)
# param_1 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2)
python3 解法, 执行用时: 2064 ms, 内存消耗: 25.1 MB, 提交时间: 2022-11-23 11:43:38
class NumMatrix:
'''
一维前缀和
'''
def __init__(self, matrix: List[List[int]]):
m, n = len(matrix), (len(matrix[0]) if matrix else 0)
self.sums = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m)]
_sums = self.sums
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
_sums[i][j + 1] = _sums[i][j] + matrix[i][j]
def sumRegion(self, row1: int, col1: int, row2: int, col2: int) -> int:
_sums = self.sums
total = sum(_sums[i][col2 + 1] - _sums[i][col1] for i in range(row1, row2 + 1))
return total
# Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumMatrix(matrix)
# param_1 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2)