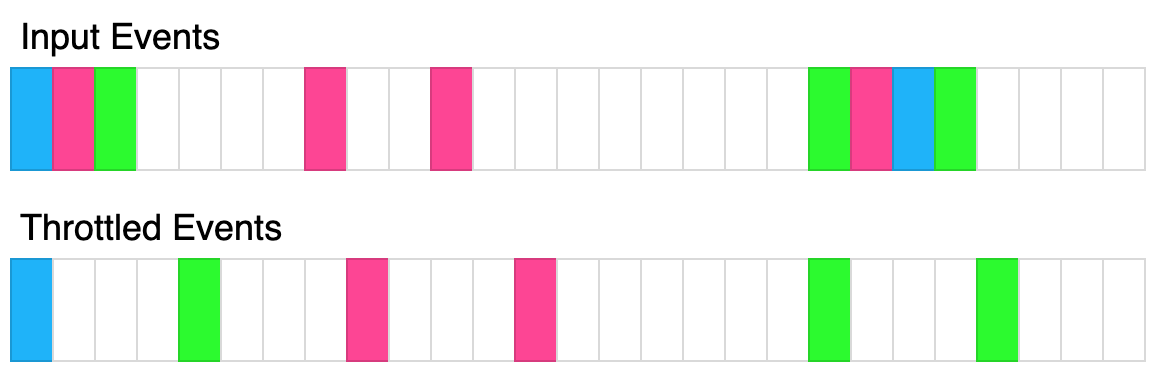
/**
* @param {Function} queryMultiple
* @param {number} t
* @return {void}
*/
var QueryBatcher = function(queryMultiple, t) {
};
/**
* @param {string} key
* @return {Promise<string>}
*/
QueryBatcher.prototype.getValue = async function(key) {
};
/**
* async function queryMultiple(keys) {
·* return keys.map(key => key + '!');
* }
*
* const batcher = new QueryBatcher(queryMultiple, 100);
* batcher.getValue('a').then(console.log); // resolves "a!" at t=0ms
* batcher.getValue('b').then(console.log); // resolves "b!" at t=100ms
* batcher.getValue('c').then(console.log); // resolves "c!" at t=100ms
*/