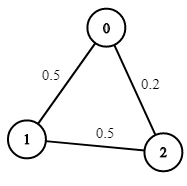
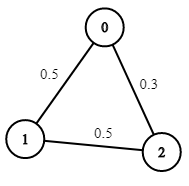
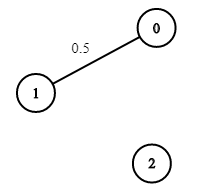
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) {
}
};
golang 解法, 执行用时: 104 ms, 内存消耗: 7.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-26 20:14:56
func maxProbability(n int, edges [][]int, succProb []float64, start int, end int) float64 {
graph := make([][]state, n)
for i:=0; i<len(edges); i++ { //创建图
edge := edges[i]
graph[edge[0]] = append(graph[edge[0]], state{edge[1], succProb[i]})
graph[edge[1]] = append(graph[edge[1]], state{edge[0], succProb[i]})
}
dist := make([]float64, n) //最大距离数组
dist[start] = 1
h := &hp{{start, 1}}
for 0 < h.Len() {
cur := heap.Pop(h).(state)
if cur.id == end { //如果找到end节点,直接返回
return cur.dist
}
if cur.dist < dist[cur.id] { //如果当前路径小于最大距离,则舍弃
continue
}
for _, next := range graph[cur.id] {
if d := cur.dist * next.dist; d > dist[next.id] { //如果从start到cur节点再到next节点的距离大于已知start到next最大距离,则更新
dist[next.id] = d
heap.Push(h, state{next.id, d})
}
}
}
return dist[end]
}
type state struct {
id int
dist float64
}
// 大根堆
type hp []state
func (h hp) Len() int {return len(h)}
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool {return h[i].dist > h[j].dist} //注意这个地方
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) {h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i]}
func (h *hp) Push(v interface{}) {*h = append(*h, v.(state))}
func (h *hp) Pop() (v interface{}) {
*h, v = (*h)[:h.Len()-1],(*h)[h.Len()-1]
return
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 192 ms, 内存消耗: 26.4 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-26 20:14:31
class Solution:
def maxProbability(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], succProb: List[float], start: int, end: int) -> float:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i, (x, y) in enumerate(edges):
graph[x].append((succProb[i], y))
graph[y].append((succProb[i], x))
que = [(-1.0, start)]
prob = [0.0] * n
prob[start] = 1.0
while que:
pr, node = heapq.heappop(que)
pr = -pr
if pr < prob[node]:
continue
for prNext, nodeNext in graph[node]:
if prob[nodeNext] < prob[node] * prNext:
prob[nodeNext] = prob[node] * prNext
heapq.heappush(que, (-prob[nodeNext], nodeNext))
return prob[end]
java 解法, 执行用时: 34 ms, 内存消耗: 53.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-26 20:14:08
class Solution {
public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) {
List<List<Pair>> graph = new ArrayList<List<Pair>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Pair>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int[] e = edges[i];
graph.get(e[0]).add(new Pair(succProb[i], e[1]));
graph.get(e[1]).add(new Pair(succProb[i], e[0]));
}
PriorityQueue<Pair> que = new PriorityQueue<Pair>();
double[] prob = new double[n];
que.offer(new Pair(1, start));
prob[start] = 1;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
Pair pair = que.poll();
double pr = pair.probability;
int node = pair.node;
if (pr < prob[node]) {
continue;
}
for (Pair pairNext : graph.get(node)) {
double prNext = pairNext.probability;
int nodeNext = pairNext.node;
if (prob[nodeNext] < prob[node] * prNext) {
prob[nodeNext] = prob[node] * prNext;
que.offer(new Pair(prob[nodeNext], nodeNext));
}
}
}
return prob[end];
}
}
class Pair implements Comparable<Pair> {
double probability;
int node;
public Pair(double probability, int node) {
this.probability = probability;
this.node = node;
}
public int compareTo(Pair pair2) {
if (this.probability == pair2.probability) {
return this.node - pair2.node;
} else {
return this.probability - pair2.probability > 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
}
}
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 156 ms, 内存消耗: 65.2 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-26 20:13:55
class Solution {
public:
// Djikstra 算法
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) {
vector<vector<pair<double, int>>> graph(n);
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
auto& e = edges[i];
graph[e[0]].emplace_back(succProb[i], e[1]);
graph[e[1]].emplace_back(succProb[i], e[0]);
}
priority_queue<pair<double, int>> que;
vector<double> prob(n, 0);
que.emplace(1, start);
prob[start] = 1;
while (!que.empty()) {
auto [pr, node] = que.top();
que.pop();
if (pr < prob[node]) {
continue;
}
for (auto& [prNext, nodeNext] : graph[node]) {
if (prob[nodeNext] < prob[node] * prNext) {
prob[nodeNext] = prob[node] * prNext;
que.emplace(prob[nodeNext], nodeNext);
}
}
}
return prob[end];
}
};