C++
Java
Python
Python3
C
C#
JavaScript
Ruby
Swift
Go
Scala
Kotlin
Rust
PHP
TypeScript
Racket
Erlang
Elixir
Dart
monokai
ambiance
chaos
chrome
cloud9_day
cloud9_night
cloud9_night_low_color
clouds
clouds_midnight
cobalt
crimson_editor
dawn
dracula
dreamweaver
eclipse
github
github_dark
gob
gruvbox
gruvbox_dark_hard
gruvbox_light_hard
idle_fingers
iplastic
katzenmilch
kr_theme
kuroir
merbivore
merbivore_soft
mono_industrial
nord_dark
one_dark
pastel_on_dark
solarized_dark
solarized_light
sqlserver
terminal
textmate
tomorrow
tomorrow_night
tomorrow_night_blue
tomorrow_night_bright
tomorrow_night_eighties
twilight
vibrant_ink
xcode
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
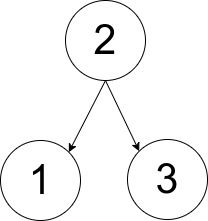
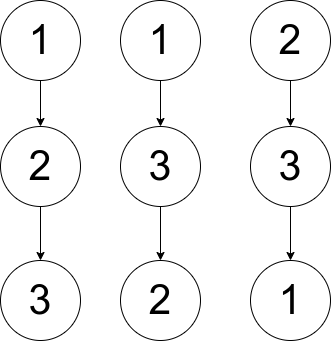
int checkWays(vector<vector<int>>& pairs) {
}
};
运行代码
提交
golang 解法, 执行用时: 436 ms, 内存消耗: 22.4 MB, 提交时间: 2023-06-14 09:41:38
func checkWays(pairs [][]int) int {
adj := map[int]map[int]bool{}
for _, p := range pairs {
x, y := p[0], p[1]
if adj[x] == nil {
adj[x] = map[int]bool{}
}
adj[x][y] = true
if adj[y] == nil {
adj[y] = map[int]bool{}
}
adj[y][x] = true
}
// 检测是否存在根节点
root := -1
for node, neighbours := range adj {
if len(neighbours) == len(adj)-1 {
root = node
break
}
}
if root == -1 {
return 0
}
ans := 1
for node, neighbours := range adj {
if node == root {
continue
}
currDegree := len(neighbours)
parent := -1
parentDegree := math.MaxInt32
// 根据 degree 的大小找到 node 的父节点 parent
for neighbour := range neighbours {
if len(adj[neighbour]) < parentDegree && len(adj[neighbour]) >= currDegree {
parent = neighbour
parentDegree = len(adj[neighbour])
}
}
if parent == -1 {
return 0
}
// 检测 neighbours 是否为 adj[parent] 的子集
for neighbour := range neighbours {
if neighbour != parent && !adj[parent][neighbour] {
return 0
}
}
if parentDegree == currDegree {
ans = 2
}
}
return ans
}
javascript 解法, 执行用时: 284 ms, 内存消耗: 77.6 MB, 提交时间: 2023-06-14 09:40:42
/**
* @param {number[][]} pairs
* @return {number}
*/
var checkWays = function(pairs) {
const adj = new Map();
for (const p of pairs) {
if (!adj.has(p[0])) {
adj.set(p[0], new Set());
}
if (!adj.has(p[1])) {
adj.set(p[1], new Set());
}
adj.get(p[0]).add(p[1]);
adj.get(p[1]).add(p[0]);
}
/* 检测是否存在根节点*/
let root = -1;
const entries = new Set();
for (const entry of adj.entries()) {
entries.add(entry);
}
for (const [node, neg] of entries) {
if (neg.size === adj.size - 1) {
root = node;
}
}
if (root === -1) {
return 0;
}
let res = 1;
for (const [node, neg] of entries) {
/* 如果当前节点为根节点 */
if (root === node) {
continue;
}
const currDegree = neg.size;
let parentNode = -1;
let parentDegree = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
/* 根据degree的大小找到当前节点的父节点 */
for (const neighbour of neg) {
if (adj.has(neighbour) && adj.get(neighbour).size < parentDegree && adj.get(neighbour).size >= currDegree) {
parentNode = neighbour;
parentDegree = adj.get(neighbour).size;
}
}
if (parentNode === -1) {
return 0;
}
/* 检测父节点的集合是否包含所有的孩子节点 */
for (const neighbour of neg) {
if (neighbour === parentNode) {
continue;
}
if (!adj.get(parentNode).has(neighbour)) {
return 0;
}
}
if (parentDegree === currDegree) {
res = 2;
}
}
return res;
};
java 解法, 执行用时: 130 ms, 内存消耗: 72.1 MB, 提交时间: 2023-06-14 09:40:24
class Solution {
public int checkWays(int[][] pairs) {
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> adj = new HashMap<Integer, Set<Integer>>();
for (int[] p : pairs) {
adj.putIfAbsent(p[0], new HashSet<Integer>());
adj.putIfAbsent(p[1], new HashSet<Integer>());
adj.get(p[0]).add(p[1]);
adj.get(p[1]).add(p[0]);
}
/* 检测是否存在根节点*/
int root = -1;
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Set<Integer>>> entries = adj.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Set<Integer>> entry : entries) {
int node = entry.getKey();
Set<Integer> neighbours = entry.getValue();
if (neighbours.size() == adj.size() - 1) {
root = node;
}
}
if (root == -1) {
return 0;
}
int res = 1;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Set<Integer>> entry : entries) {
int node = entry.getKey();
Set<Integer> neighbours = entry.getValue();
if (node == root) {
continue;
}
int currDegree = neighbours.size();
int parent = -1;
int parentDegree = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/* 根据 degree 的大小找到 node 的父节点 parent */
for (int neighbour : neighbours) {
if (adj.get(neighbour).size() < parentDegree && adj.get(neighbour).size() >= currDegree) {
parent = neighbour;
parentDegree = adj.get(neighbour).size();
}
}
if (parent == -1) {
return 0;
}
/* 检测 neighbours 是否是 adj[parent] 的子集 */
for (int neighbour : neighbours) {
if (neighbour == parent) {
continue;
}
if (!adj.get(parent).contains(neighbour)) {
return 0;
}
}
if (parentDegree == currDegree) {
res = 2;
}
}
return res;
}
}
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 756 ms, 内存消耗: 159.6 MB, 提交时间: 2023-06-14 09:40:09
class Solution {
public:
int checkWays(vector<vector<int>>& pairs) {
unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> adj;
for (auto &p : pairs) {
adj[p[0]].emplace(p[1]);
adj[p[1]].emplace(p[0]);
}
/* 检测是否存在根节点*/
int root = -1;
for (auto &[node, neighbours] : adj) {
if (neighbours.size() == adj.size() - 1) {
root = node;
break;
}
}
if (root == -1) {
return 0;
}
int res = 1;
for (auto &[node, neighbours] : adj) {
if (node == root) {
continue;
}
int currDegree = neighbours.size();
int parent = -1;
int parentDegree = INT_MAX;
/* 根据 degree 的大小找到 node 的父节点 parent */
for (auto &neighbour : neighbours) {
if (adj[neighbour].size() < parentDegree && adj[neighbour].size() >= currDegree) {
parent = neighbour;
parentDegree = adj[neighbour].size();
}
}
if (parent == -1) {
return 0;
}
/* 检测 neighbours 是否是 adj[parent] 的子集 */
for (auto &neighbour : neighbours) {
if (neighbour == parent) {
continue;
}
if (!adj[parent].count(neighbour)) {
return 0;
}
}
if (parentDegree == currDegree) {
res = 2;
}
}
return res;
}
};
python3 解法, 执行用时: 332 ms, 内存消耗: 45.2 MB, 提交时间: 2023-06-14 09:39:43
# 直接模拟
class Solution:
def checkWays(self, pairs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
adj = defaultdict(set)
for x, y in pairs:
adj[x].add(y)
adj[y].add(x)
# 检测是否存在根节点
root = next((node for node, neighbours in adj.items() if len(neighbours) == len(adj) - 1), -1)
if root == -1:
return 0
ans = 1
for node, neighbours in adj.items():
if node == root:
continue
currDegree = len(neighbours)
parent = -1
parentDegree = maxsize
# 根据 degree 的大小找到 node 的父节点 parent
for neighbour in neighbours:
if currDegree <= len(adj[neighbour]) < parentDegree:
parent = neighbour
parentDegree = len(adj[neighbour])
# 检测 neighbours 是否为 adj[parent] 的子集
if parent == -1 or any(neighbour != parent and neighbour not in adj[parent] for neighbour in neighbours):
return 0
if parentDegree == currDegree:
ans = 2
return ans
java 解法, 执行用时: 174 ms, 内存消耗: 83.2 MB, 提交时间: 2023-06-14 09:38:08
class Solution {
public int checkWays(int[][] pairs) {
//1. 构建图
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] pair:pairs){
graph.putIfAbsent(pair[0],new HashSet<>());
graph.putIfAbsent(pair[1],new HashSet<>());
graph.get(pair[0]).add(pair[1]);
graph.get(pair[1]).add(pair[0]);
}
int n = graph.keySet().size();
int root = -1;
//2. 所有人的祖先就是先祖(唐太祖,只有最上面那一辈叫祖)
for(int key:graph.keySet()){
int size = graph.get(key).size();
if(size == n-1){
root = key;
}
}
if(root == -1)
return 0;
int ans = 1;
for(Integer node:graph.keySet()){
if(node == root) continue;
Set<Integer> neighbours = graph.get(node);
int size = graph.get(node).size();
int parent = -1;
int pSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//3. 找自己的爹,和自己关联的后代比自己多的可能是自己爹,也可能是先祖
//爹就刚刚好跟我关联,且后辈比我多,比祖宗少(宗代表先辈非最上一辈)
for(Integer neighbour:neighbours){
if(graph.get(neighbour).size()<pSize && size <= graph.get(neighbour).size()){
parent = neighbour;
pSize = graph.get(neighbour).size();
}
}
if(parent==-1)
return 0;
//3. 既然跟我关联的,确认了爹,那其他要么是兄弟,要么是子女,要么是祖宗
//那我爹的先辈后辈,必然包含了我的先辈后辈(我的后辈应该比父辈少)
Set<Integer> tmp = new HashSet<>(graph.get(parent));
tmp.add(parent);
//4. 如果不能完全包含,说明父子关系不成立
if(!tmp.containsAll(neighbours))
return 0;
//5. 父子关系成立,不一定谁父谁子,那如果有结果,那就不止一种
// 注意不能直接返回,其他点验证不通过的情况,可能返回0
if(pSize == size){
ans = 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
}