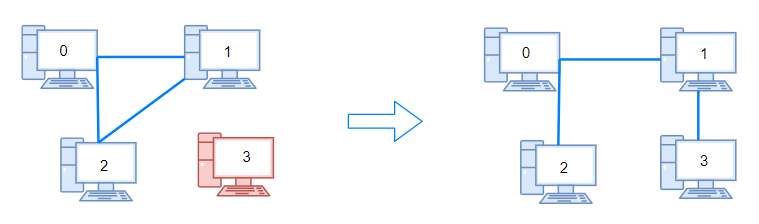
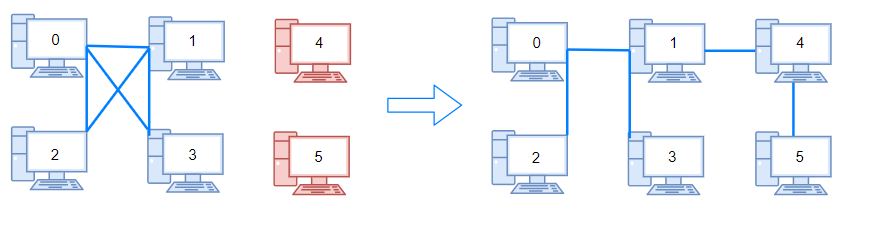
C++
Java
Python
Python3
C
C#
JavaScript
Ruby
Swift
Go
Scala
Kotlin
Rust
PHP
TypeScript
Racket
Erlang
Elixir
Dart
monokai
ambiance
chaos
chrome
cloud9_day
cloud9_night
cloud9_night_low_color
clouds
clouds_midnight
cobalt
crimson_editor
dawn
dracula
dreamweaver
eclipse
github
github_dark
gob
gruvbox
gruvbox_dark_hard
gruvbox_light_hard
idle_fingers
iplastic
katzenmilch
kr_theme
kuroir
merbivore
merbivore_soft
mono_industrial
nord_dark
one_dark
pastel_on_dark
solarized_dark
solarized_light
sqlserver
terminal
textmate
tomorrow
tomorrow_night
tomorrow_night_blue
tomorrow_night_bright
tomorrow_night_eighties
twilight
vibrant_ink
xcode
上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
}
};
运行代码
提交
python3 解法, 执行用时: 132 ms, 内存消耗: 26.2 MB, 提交时间: 2022-08-01 10:29:54
# 并查集模板
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n: int):
self.parent = list(range(n))
self.size = [1] * n
self.n = n
# 当前连通分量数目
self.setCount = n
def findset(self, x: int) -> int:
if self.parent[x] == x:
return x
self.parent[x] = self.findset(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def unite(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
x, y = self.findset(x), self.findset(y)
if x == y:
return False
if self.size[x] < self.size[y]:
x, y = y, x
self.parent[y] = x
self.size[x] += self.size[y]
self.setCount -= 1
return True
def connected(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
x, y = self.findset(x), self.findset(y)
return x == y
class Solution:
def makeConnected(self, n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(connections) < n - 1:
return -1
uf = UnionFind(n)
for x, y in connections:
uf.unite(x, y)
return uf.setCount - 1
python3 解法, 执行用时: 160 ms, 内存消耗: 46.4 MB, 提交时间: 2022-08-01 10:29:10
class Solution:
def makeConnected(self, n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(connections) < n - 1:
return -1
edges = collections.defaultdict(list)
for x, y in connections:
edges[x].append(y)
edges[y].append(x)
seen = set()
def dfs(u: int):
seen.add(u)
for v in edges[u]:
if v not in seen:
dfs(v)
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in seen:
dfs(i)
ans += 1
return ans - 1