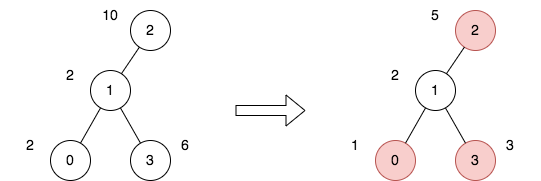
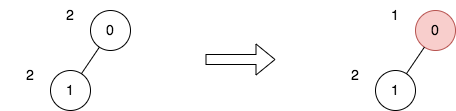
rust 解法, 执行用时: 8 ms, 内存消耗: 2.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-12-06 07:41:03
impl Solution {
pub fn minimum_total_price(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, price: Vec<i32>, trips: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for e in &edges {
let x = e[0] as usize;
let y = e[1] as usize;
g[x].push(y);
g[y].push(x);
}
fn dfs(x: usize, fa: usize, cnt: &mut Vec<i32>, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, end: usize) -> bool {
if x == end {
cnt[x] += 1;
return true; // 找到 end
}
for &y in &g[x] {
if y != fa && dfs(y, x, cnt, g, end) {
cnt[x] += 1; // x 是 end 的祖先节点,也就在路径上
return true;
}
}
false // 未找到 end
}
let mut cnt = vec![0; n];
for t in &trips {
dfs(t[0] as usize, n, &mut cnt, &g, t[1] as usize);
}
// 类似 337. 打家劫舍 III
fn dp(x: usize, fa: usize, price: &Vec<i32>, cnt: &Vec<i32>, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>) -> (i32, i32) {
let mut not_halve = price[x] * cnt[x]; // x 不变
let mut halve = not_halve / 2; // x 减半
for &y in &g[x] {
if y != fa {
let (nh, h) = dp(y, x, price, cnt, g); // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
not_halve += nh.min(h); // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变或者减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh; // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
}
}
(not_halve, halve)
}
let (nh, h) = dp(0, 0, &price, &cnt, &g);
nh.min(h)
}
}
rust 解法, 执行用时: 8 ms, 内存消耗: 2.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-12-06 07:40:50
impl Solution {
pub fn minimum_total_price(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, price: Vec<i32>, trips: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for e in &edges {
let x = e[0] as usize;
let y = e[1] as usize;
g[x].push(y);
g[y].push(x);
}
let mut qs = vec![vec![]; n];
for t in &trips {
let s = t[0] as usize;
let e = t[1] as usize;
qs[s].push(e); // 路径端点分组
if s != e {
qs[e].push(s);
}
}
// 并查集模板
let mut root: Vec<usize> = (0..n).collect();
fn find(x: usize, root: &mut Vec<usize>) -> usize {
if x != root[x] {
root[x] = find(root[x], root);
}
root[x]
}
let mut diff = vec![0; n];
let mut father = vec![0; n];
let mut color = vec![0; n];
fn tarjan(x: usize, fa: usize, diff: &mut Vec<i32>, father: &mut Vec<usize>, color: &mut Vec<i32>, root: &mut Vec<usize>, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, qs: &Vec<Vec<usize>>) {
father[x] = fa;
color[x] = 1; // 递归中
for &y in &g[x] {
if color[y] == 0 { // 未递归
tarjan(y, x, diff, father, color, root, g, qs);
root[y] = x; // 相当于把 y 的子树节点全部 merge 到 x
}
}
for &y in &qs[x] {
// color[y] == 2 意味着 y 所在子树已经遍历完
// 也就意味着 y 已经 merge 到它和 x 的 lca 上了
// 此时 find(y) 就是 x 和 y 的 lca
if y == x || color[y] == 2 {
diff[x] += 1;
diff[y] += 1;
let lca = find(y, root);
diff[lca] -= 1;
if father[lca] != g.len() {
diff[father[lca]] -= 1;
}
}
}
color[x] = 2; // 递归结束
}
tarjan(0, n, &mut diff, &mut father, &mut color, &mut root, &g, &qs);
fn dfs(x: usize, fa: usize, price: &Vec<i32>, diff: &Vec<i32>, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>) -> (i32, i32, i32) {
let mut not_halve = 0;
let mut halve = 0;
let mut cnt = diff[x];
for &y in &g[x] {
if y != fa {
let (nh, h, c) = dfs(y, x, price, diff, g); // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
not_halve += nh.min(h); // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh; // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
cnt += c; // 自底向上累加差分值
}
}
not_halve += price[x] * cnt; // x 不变
halve += price[x] * cnt / 2; // x 减半
(not_halve, halve, cnt)
}
let (nh, h, _) = dfs(0, 0, &price, &diff, &g);
nh.min(h)
}
}
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 36 ms, 内存消耗: 39.7 MB, 提交时间: 2023-12-06 07:40:31
class Solution {
public:
int minimumTotalPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>> &edges, vector<int> &price, vector<vector<int>> &trips) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto &e: edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x); // 建树
}
vector<vector<int>> qs(n);
for (auto &t: trips) {
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
qs[x].push_back(y); // 路径端点分组
if (x != y) {
qs[y].push_back(x);
}
}
// 并查集模板
vector<int> root(n);
iota(root.begin(), root.end(), 0);
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) -> int { return root[x] == x ? x : root[x] = find(root[x]); };
vector<int> diff(n), father(n), color(n);
function<void(int, int)> tarjan = [&](int x, int fa) {
father[x] = fa;
color[x] = 1; // 递归中
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (color[y] == 0) { // 未递归
tarjan(y, x);
root[y] = x; // 相当于把 y 的子树节点全部 merge 到 x
}
}
for (int y: qs[x]) {
// color[y] == 2 意味着 y 所在子树已经遍历完
// 也就意味着 y 已经 merge 到它和 x 的 lca 上了
// 此时 find(y) 就是 x 和 y 的 lca
if (y == x || color[y] == 2) {
diff[x]++;
diff[y]++;
int lca = find(y);
diff[lca]--;
int f = father[lca];
if (f >= 0) {
diff[f]--;
}
}
}
color[x] = 2; // 递归结束
};
tarjan(0, -1);
function<tuple<int, int, int>(int, int)> dfs = [&](int x, int fa) -> tuple<int, int, int> {
int not_halve = 0, halve = 0, cnt = diff[x];
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa) {
auto [nh, h, c] = dfs(y, x); // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
not_halve += min(nh, h); // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh; // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
cnt += c; // 自底向上累加差分值
}
}
not_halve += price[x] * cnt; // x 不变
halve += price[x] * cnt / 2; // x 减半
return {not_halve, halve, cnt};
};
auto [nh, h, _] = dfs(0, -1);
return min(nh, h);
}
};
cpp 解法, 执行用时: 40 ms, 内存消耗: 39.1 MB, 提交时间: 2023-12-06 07:40:07
class Solution {
public:
int minimumTotalPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>> &edges, vector<int> &price, vector<vector<int>> &trips) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto &e: edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x); // 建树
}
vector<int> cnt(n);
for (auto &t: trips) {
int end = t[1];
function<bool(int, int)> dfs = [&](int x, int fa) -> bool {
if (x == end) {
cnt[x]++;
return true; // 找到 end
}
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa && dfs(y, x)) {
cnt[x]++; // x 是 end 的祖先节点,也就在路径上
return true;
}
}
return false; // 未找到 end
};
dfs(t[0], -1);
}
// 类似 337. 打家劫舍 III
function<pair<int, int>(int, int)> dfs = [&](int x, int fa) -> pair<int, int> {
int not_halve = price[x] * cnt[x]; // x 不变
int halve = not_halve / 2; // x 减半
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa) {
auto [nh, h] = dfs(y, x); // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
not_halve += min(nh, h); // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh; // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
}
}
return {not_halve, halve};
};
auto [nh, h] = dfs(0, -1);
return min(nh, h);
}
};
python3 解法, 执行用时: 64 ms, 内存消耗: 15.2 MB, 提交时间: 2023-04-17 16:48:02
class Solution:
def minimumTotalPrice(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], price: List[int], trips: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y in edges:
g[x].append(y)
g[y].append(x) # 建树
qs = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for s, e in trips:
qs[s].append(e) # 路径端点分组
if s != e:
qs[e].append(s)
# 并查集模板
pa = list(range(n))
def find(x: int) -> int:
if x != pa[x]:
pa[x] = find(pa[x])
return pa[x]
diff = [0] * n
father = [0] * n
color = [0] * n
def tarjan(x: int, fa: int) -> None:
father[x] = fa
color[x] = 1 # 递归中
for y in g[x]:
if color[y] == 0: # 未递归
tarjan(y, x)
pa[y] = x # 相当于把 y 的子树节点全部 merge 到 x
for y in qs[x]:
# color[y] == 2 意味着 y 所在子树已经遍历完
# 也就意味着 y 已经 merge 到它和 x 的 lca 上了
if y == x or color[y] == 2: # 从 y 向上到达 lca 然后拐弯向下到达 x
diff[x] += 1
diff[y] += 1
lca = find(y)
diff[lca] -= 1
if father[lca] >= 0:
diff[father[lca]] -= 1
color[x] = 2 # 递归结束
tarjan(0, -1)
def dfs(x: int, fa: int) -> (int, int, int):
not_halve, halve, cnt = 0, 0, diff[x]
for y in g[x]:
if y != fa:
nh, h, c = dfs(y, x) # 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
not_halve += min(nh, h) # x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh # x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
cnt += c # 自底向上累加差分值
not_halve += price[x] * cnt # x 不变
halve += price[x] * cnt // 2 # x 减半
return not_halve, halve, cnt
return min(dfs(0, -1)[:2])
java 解法, 执行用时: 6 ms, 内存消耗: 41.5 MB, 提交时间: 2023-04-17 16:47:39
class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g, qs;
private int[] diff, father, color, price;
public int minimumTotalPrice(int n, int[][] edges, int[] price, int[][] trips) {
g = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].add(y);
g[y].add(x); // 建树
}
qs = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(qs, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var t : trips) {
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
qs[x].add(y); // 路径端点分组
if (x != y) qs[y].add(x);
}
pa = new int[n];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
pa[i] = i;
diff = new int[n];
father = new int[n];
color = new int[n];
tarjan(0, -1);
this.price = price;
var p = dfs(0, -1);
return Math.min(p[0], p[1]);
}
// 并查集模板
private int[] pa;
private int find(int x) {
if (pa[x] != x)
pa[x] = find(pa[x]);
return pa[x];
}
private void tarjan(int x, int fa) {
father[x] = fa;
color[x] = 1; // 递归中
for (int y : g[x])
if (color[y] == 0) { // 未递归
tarjan(y, x);
pa[y] = x; // 相当于把 y 的子树节点全部 merge 到 x
}
for (int y : qs[x])
// color[y] == 2 意味着 y 所在子树已经遍历完
// 也就意味着 y 已经 merge 到它和 x 的 lca 上了
if (y == x || color[y] == 2) { // 从 y 向上到达 lca 然后拐弯向下到达 x
++diff[x];
++diff[y];
int lca = find(y);
--diff[lca];
int f = father[lca];
if (f >= 0) {
--diff[f];
}
}
color[x] = 2; // 递归结束
}
private int[] dfs(int x, int fa) {
int notHalve = 0, halve = 0, cnt = diff[x];
for (int y : g[x])
if (y != fa) {
var p = dfs(y, x); // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
notHalve += Math.min(p[0], p[1]); // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += p[0]; // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
cnt += p[2]; // 自底向上累加差分值
}
notHalve += price[x] * cnt; // x 不变
halve += price[x] * cnt / 2; // x 减半
return new int[]{notHalve, halve, cnt};
}
}
golang 解法, 执行用时: 36 ms, 内存消耗: 6.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-04-17 16:47:26
func minimumTotalPrice(n int, edges [][]int, price []int, trips [][]int) int {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
x, y := e[0], e[1]
g[x] = append(g[x], y)
g[y] = append(g[y], x) // 建树
}
qs := make([][]int, n)
for _, t := range trips {
x, y := t[0], t[1]
qs[x] = append(qs[x], y) // 路径端点分组
if x != y {
qs[y] = append(qs[y], x)
}
}
// 并查集模板
pa := make([]int, n)
for i := range pa {
pa[i] = i
}
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if pa[x] != x {
pa[x] = find(pa[x])
}
return pa[x]
}
diff := make([]int, n)
father := make([]int, n)
color := make([]int8, n)
var tarjan func(int, int)
tarjan = func(x, fa int) {
father[x] = fa
color[x] = 1 // 递归中
for _, y := range g[x] {
if color[y] == 0 { // 未递归
tarjan(y, x)
pa[y] = x // 相当于把 y 的子树节点全部 merge 到 x
}
}
for _, y := range qs[x] {
// color[y] == 2 意味着 y 所在子树已经遍历完
// 也就意味着 y 已经 merge 到它和 x 的 lca 上了
if y == x || color[y] == 2 { // 从 y 向上到达 lca 然后拐弯向下到达 x
diff[x]++
diff[y]++
lca := find(y)
diff[lca]--
if f := father[lca]; f >= 0 {
diff[f]--
}
}
}
color[x] = 2 // 递归结束
}
tarjan(0, -1)
var dfs func(int, int) (int, int, int)
dfs = func(x, fa int) (notHalve, halve, cnt int) {
cnt = diff[x]
for _, y := range g[x] {
if y != fa {
nh, h, c := dfs(y, x) // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
notHalve += min(nh, h) // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
cnt += c // 自底向上累加差分值
}
}
notHalve += price[x] * cnt // x 不变
halve += price[x] * cnt / 2 // x 减半
return
}
nh, h, _ := dfs(0, -1)
return min(nh, h)
}
func min(a, b int) int { if a > b { return b }; return a }
golang 解法, 执行用时: 28 ms, 内存消耗: 6.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-04-17 16:47:17
func minimumTotalPrice(n int, edges [][]int, price []int, trips [][]int) int {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
x, y := e[0], e[1]
g[x] = append(g[x], y)
g[y] = append(g[y], x) // 建树
}
cnt := make([]int, n)
for _, t := range trips {
end := t[1]
var dfs func(int, int) bool
dfs = func(x, fa int) bool {
if x == end { // 到达终点(注意树只有唯一的一条简单路径)
cnt[x]++ // 统计从 start 到 end 的路径上的点经过了多少次
return true // 找到终点
}
for _, y := range g[x] {
if y != fa && dfs(y, x) {
cnt[x]++ // 统计从 start 到 end 的路径上的点经过了多少次
return true
}
}
return false // 未找到终点
}
dfs(t[0], -1)
}
// 类似 337. 打家劫舍 III https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-iii/
var dfs func(int, int) (int, int)
dfs = func(x, fa int) (int, int) {
notHalve := price[x] * cnt[x] // x 不变
halve := notHalve / 2 // x 减半
for _, y := range g[x] {
if y != fa {
nh, h := dfs(y, x) // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
notHalve += min(nh, h) // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
}
}
return notHalve, halve
}
nh, h := dfs(0, -1)
return min(nh, h)
}
func min(a, b int) int { if a > b { return b }; return a }
java 解法, 执行用时: 10 ms, 内存消耗: 41.7 MB, 提交时间: 2023-04-17 16:46:51
class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] price, cnt;
private int end;
public int minimumTotalPrice(int n, int[][] edges, int[] price, int[][] trips) {
g = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].add(y);
g[y].add(x); // 建树
}
this.price = price;
cnt = new int[n];
for (var t : trips) {
end = t[1];
path(t[0], -1);
}
var p = dfs(0, -1);
return Math.min(p[0], p[1]);
}
private boolean path(int x, int fa) {
if (x == end) { // 到达终点(注意树只有唯一的一条简单路径)
++cnt[x]; // 统计从 start 到 end 的路径上的点经过了多少次
return true; // 找到终点
}
for (var y : g[x])
if (y != fa && path(y, x)) {
++cnt[x]; // 统计从 start 到 end 的路径上的点经过了多少次
return true; // 找到终点
}
return false; // 未找到终点
}
// 类似 337. 打家劫舍 III https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-iii/
private int[] dfs(int x, int fa) {
int notHalve = price[x] * cnt[x]; // x 不变
int halve = notHalve / 2; // x 减半
for (var y : g[x])
if (y != fa) {
var p = dfs(y, x); // 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
notHalve += Math.min(p[0], p[1]); // x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += p[0]; // x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
}
return new int[]{notHalve, halve};
}
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 104 ms, 内存消耗: 15.2 MB, 提交时间: 2023-04-17 16:46:31
class Solution:
def minimumTotalPrice(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], price: List[int], trips: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y in edges:
g[x].append(y)
g[y].append(x) # 建树
cnt = [0] * n
for start, end in trips:
def dfs(x: int, fa: int) -> bool:
if x == end: # 到达终点(注意树只有唯一的一条简单路径)
cnt[x] += 1 # 统计从 start 到 end 的路径上的点经过了多少次
return True # 找到终点
for y in g[x]:
if y != fa and dfs(y, x):
cnt[x] += 1 # 统计从 start 到 end 的路径上的点经过了多少次
return True # 找到终点
return False # 未找到终点
dfs(start, -1)
# 类似 337. 打家劫舍 III https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-iii/
def dfs(x: int, fa: int) -> (int, int):
not_halve = price[x] * cnt[x] # x 不变
halve = not_halve // 2 # x 减半
for y in g[x]:
if y != fa:
nh, h = dfs(y, x) # 计算 y 不变/减半的最小价值总和
not_halve += min(nh, h) # x 不变,那么 y 可以不变,可以减半,取这两种情况的最小值
halve += nh # x 减半,那么 y 只能不变
return not_halve, halve
return min(dfs(0, -1))