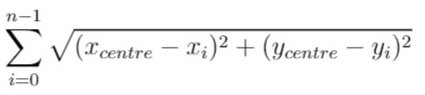上次编辑到这里,代码来自缓存 点击恢复默认模板
class Solution {
public:
double getMinDistSum(vector<vector<int>>& positions) {
}
};
java 解法, 执行用时: 66 ms, 内存消耗: 41.9 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-06 23:35:05
// 梯度下降
class Solution {
public double getMinDistSum(int[][] positions) {
double eps = 1e-7;
double alpha = 1;
double decay = 1e-3;
int n = positions.length;
// 调整批大小
int batchSize = n;
double x = 0.0, y = 0.0;
for (int[] pos : positions) {
x += pos[0];
y += pos[1];
}
x /= n;
y /= n;
while (true) {
// 将数据随机打乱
shuffle(positions);
double xPrev = x;
double yPrev = y;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += batchSize) {
int j = Math.min(i + batchSize, n);
double dx = 0.0, dy = 0.0;
// 计算导数,注意处理分母为零的情况
for (int k = i; k < j; ++k) {
int[] pos = positions[k];
dx += (x - pos[0]) / (Math.sqrt((x - pos[0]) * (x - pos[0]) + (y - pos[1]) * (y - pos[1])) + eps);
dy += (y - pos[1]) / (Math.sqrt((x - pos[0]) * (x - pos[0]) + (y - pos[1]) * (y - pos[1])) + eps);
}
x -= alpha * dx;
y -= alpha * dy;
// 每一轮迭代后,将学习率进行衰减
alpha *= (1.0 - decay);
}
// 判断是否结束迭代
if (Math.sqrt((x - xPrev) * (x - xPrev) + (y - yPrev) * (y - yPrev)) < eps) {
break;
}
}
return getDist(x, y, positions);
}
public void shuffle(int[][] positions) {
Random rand = new Random();
int n = positions.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = positions[i][0], y = positions[i][1];
int randIndex = rand.nextInt(n);
positions[i][0] = positions[randIndex][0];
positions[i][1] = positions[randIndex][1];
positions[randIndex][0] = x;
positions[randIndex][1] = y;
}
}
// 计算服务中心 (xc, yc) 到客户的欧几里得距离之和
public double getDist(double xc, double yc, int[][] positions) {
double ans = 0;
for (int[] pos : positions) {
ans += Math.sqrt((pos[0] - xc) * (pos[0] - xc) + (pos[1] - yc) * (pos[1] - yc));
}
return ans;
}
}
java 解法, 执行用时: 8 ms, 内存消耗: 39.3 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-06 23:34:38
// 爬山法
class Solution {
private static int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
public double getMinDistSum(int[][] positions) {
double eps = 1e-7;
double step = 1;
double decay = 0.5;
int n = positions.length;
double x = 0.0, y = 0.0;
for (int[] pos : positions) {
x += pos[0];
y += pos[1];
}
x /= n;
y /= n;
while (step > eps) {
boolean modified = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
double xNext = x + step * dirs[i][0];
double yNext = y + step * dirs[i][1];
if (getDist(xNext, yNext, positions) < getDist(x, y, positions)) {
x = xNext;
y = yNext;
modified = true;
break;
}
}
if (!modified) {
step *= (1.0 - decay);
}
}
return getDist(x, y, positions);
}
// 计算服务中心 (xc, yc) 到客户的欧几里得距离之和
public double getDist(double xc, double yc, int[][] positions) {
double ans = 0;
for (int[] pos : positions) {
ans += Math.sqrt((pos[0] - xc) * (pos[0] - xc) + (pos[1] - yc) * (pos[1] - yc));
}
return ans;
}
}
java 解法, 执行用时: 217 ms, 内存消耗: 38.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-06 23:34:15
// 三分查找
class Solution {
public double getMinDistSum(int[][] positions) {
double eps = 1e-7;
double xLeft = 0.0, xRight = 100.0;
while (xRight - xLeft > eps) {
// 左 1/3 点
double xFirst = (xLeft + xLeft + xRight) / 3;
// 右 1/3 点
double xSecond = (xLeft + xRight + xRight) / 3;
if (checkOptimal(xFirst, positions, eps) < checkOptimal(xSecond, positions, eps)) {
xRight = xSecond;
} else {
xLeft = xFirst;
}
}
return checkOptimal(xLeft, positions, eps);
}
// 计算服务中心 (xc, yc) 到客户的欧几里得距离之和
public double getDist(double xc, double yc, int[][] positions) {
double ans = 0;
for (int[] pos : positions) {
ans += Math.sqrt((pos[0] - xc) * (pos[0] - xc) + (pos[1] - yc) * (pos[1] - yc));
}
return ans;
}
// 固定 xc,使用三分法找出最优的 yc
public double checkOptimal(double xc, int[][] positions, double eps) {
double yLeft = 0.0, yRight = 100.0;
while (yRight - yLeft > eps) {
double yFirst = (yLeft + yLeft + yRight) / 3;
double ySecond = (yLeft + yRight + yRight) / 3;
if (getDist(xc, yFirst, positions) < getDist(xc, ySecond, positions)) {
yRight = ySecond;
} else {
yLeft = yFirst;
}
}
return getDist(xc, yLeft, positions);
}
}
python3 解法, 执行用时: 3448 ms, 内存消耗: 15.8 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-06 23:33:33
# 三分查找
class Solution:
def getMinDistSum(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> float:
eps = 1e-7
# 计算服务中心 (xc, yc) 到客户的欧几里得距离之和
getDist = lambda xc, yc: sum(((x - xc) ** 2 + (y - yc) ** 2) ** 0.5 for x, y in positions)
# 固定 xc,使用三分法找出最优的 yc
def checkOptimal(xc: float) -> float:
yLeft, yRight = 0.0, 100.0
while yRight - yLeft > eps:
yFirst = (yLeft + yLeft + yRight) / 3
ySecond = (yLeft + yRight + yRight) / 3
if getDist(xc, yFirst) < getDist(xc, ySecond):
yRight = ySecond
else:
yLeft = yFirst
return getDist(xc, yLeft)
xLeft, xRight = 0.0, 100.0
while xRight - xLeft > eps:
# 左 1/3 点
xFirst = (xLeft + xLeft + xRight) / 3
# 右 1/3 点
xSecond = (xLeft + xRight + xRight) / 3
if checkOptimal(xFirst) < checkOptimal(xSecond):
xRight = xSecond
else:
xLeft = xFirst
return checkOptimal(xLeft)
python3 解法, 执行用时: 152 ms, 内存消耗: 16.1 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-06 23:33:05
# 爬山法
class Solution:
def getMinDistSum(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> float:
dirs = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
eps = 1e-7
step = 1.0
decay = 0.5
n = len(positions)
x = sum(pos[0] for pos in positions) / n
y = sum(pos[1] for pos in positions) / n
# 计算服务中心 (xc, yc) 到客户的欧几里得距离之和
getDist = lambda xc, yc: sum(((x - xc) ** 2 + (y - yc) ** 2) ** 0.5 for x, y in positions)
while step > eps:
modified = False
for dx, dy in dirs:
xNext = x + step * dx
yNext = y + step * dy
if getDist(xNext, yNext) < getDist(x, y):
x, y = xNext, yNext
modified = True
break
if not modified:
step *= (1.0 - decay)
return getDist(x, y)
python3 解法, 执行用时: 1676 ms, 内存消耗: 16.1 MB, 提交时间: 2023-09-06 23:32:40
# 梯度下降
class Solution:
def getMinDistSum(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> float:
eps = 1e-7
alpha = 1.0
decay = 1e-3
n = len(positions)
# 调整批大小
batchSize = n
x = sum(pos[0] for pos in positions) / n
y = sum(pos[1] for pos in positions) / n
# 计算服务中心 (xc, yc) 到客户的欧几里得距离之和
getDist = lambda xc, yc: sum(((x - xc) ** 2 + (y - yc) ** 2) ** 0.5 for x, y in positions)
while True:
# 将数据随机打乱
random.shuffle(positions)
xPrev, yPrev = x, y
for i in range(0, n, batchSize):
j = min(i + batchSize, n)
dx, dy = 0.0, 0.0
# 计算导数,注意处理分母为零的情况
for k in range(i, j):
pos = positions[k]
dx += (x - pos[0]) / (sqrt((x - pos[0]) * (x - pos[0]) + (y - pos[1]) * (y - pos[1])) + eps)
dy += (y - pos[1]) / (sqrt((x - pos[0]) * (x - pos[0]) + (y - pos[1]) * (y - pos[1])) + eps)
x -= alpha * dx
y -= alpha * dy
# 每一轮迭代后,将学习率进行衰减
alpha *= (1.0 - decay)
# 判断是否结束迭代
if ((x - xPrev) ** 2 + (y - yPrev) ** 2) ** 0.5 < eps:
break
return getDist(x, y)